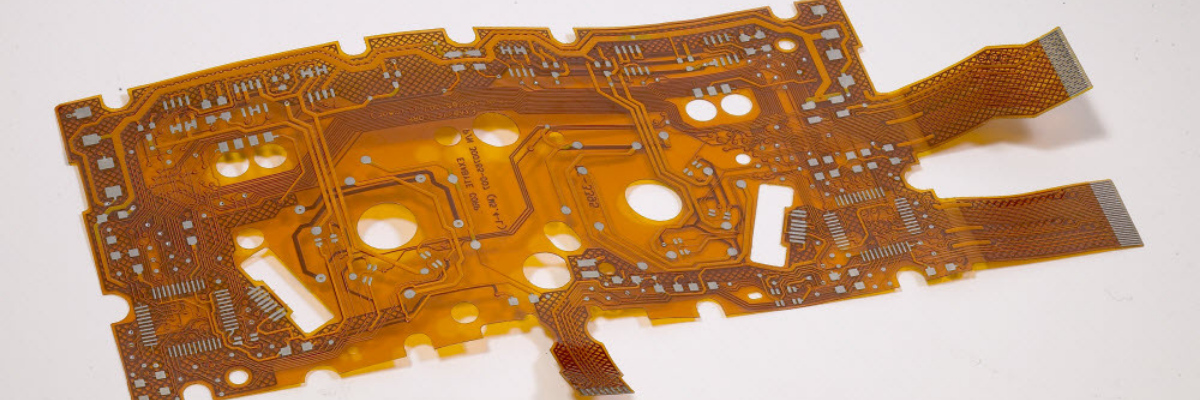
Four-layer Printed Circuit Boards or PCBs are generally used to accommodate a high number of components and circuits. They are used when there is a need for a lighter option to rigid circuit boards. Four-layer PCBs are available in a variety of types. Traditionally manufactured on a rigid board, they are now available on flexible boards as well. These flexible boards allow the PCB to be integrated in tight spaces and at a variety of angles that rigid PCBs just cannot adhere to.
Why are Flex PCBs Preferred?
When designing a component or machine with space and weight constraints, a flex PCB is a better option.
High Density of Components & Circuitry Allowed
A high density of components and circuitry can easily be accommodated in a small space in flex PCBs. Four-layered PCBs allow an increased number of components to fit onto the PCBs as both sides of a board can be used to accommodate the components. Also, the component size allowed on these boards is much smaller as compared to other PCBs. These PCBs are extremely useful when every gram in the machine matters. An assembly that is affected by the smallest change in weight can benefit from a flex PCB rather than a rigid PCB. These layers are connected by inter connectors and plated through holes.
Other Factors Contributing to the Preference of Flex PCBs
Due to the material used, they are also lighter as compared to other types of PCBs in the market. Manufacturers even have the ability to print specific numbers or names onto the PCB. This can be done to denote a manufacturing number or code, etc.
Flex PCBs also exhibit many capabilities, which can be customized according to the needs of the client. For example, flex PCBs are capable of accommodating through-hole assembly, controlled impedance, and much more while also managing thermal dissipation.
Start designing your 4-layer flex PCB to take advantage of the latest that technology has to offer.